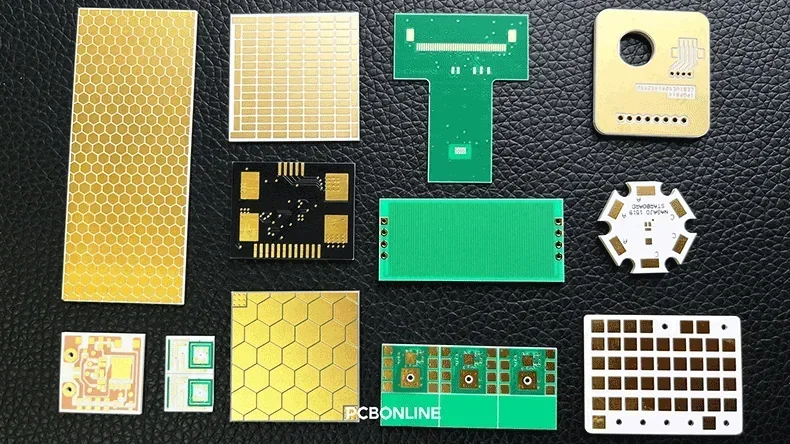
When you work on a high-power PCB that requires high thermal conductivity, you may use aluminum or copper-core PCB. However, ceramic PCBs offer much better thermal dissipation. Besides, ceramics don't oxidize or deform and feature excellent dielectric performance and precise impedance control.
So why not learn about ceramic PCB boards, including what they are, their types, manufacturing, and applications?
What are Ceramic PCB Boards?
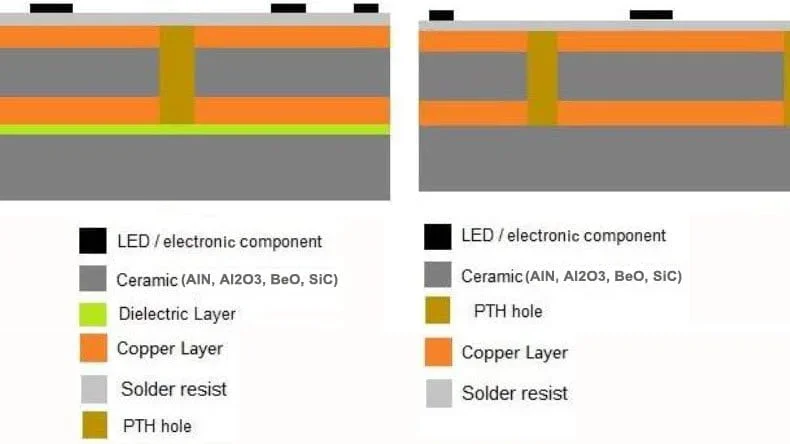
Ceramic PCB boards are printed circuit boards using aluminum nitride (AlN), aluminum oxide (Al2O3 or alumina), or beryllium oxide (BeO) as the substrate material.
In ceramic PCB manufacturing, the copper layers are plated, sintered, sputtered, or bonded on the ceramic substrate.
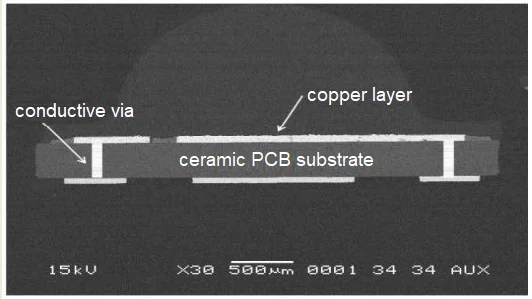
Between the copper layer and the ceramic substrate, there can be a prepreg layer to attach them, with the lamination temperatures at 200℃-300℃.
For a ceramic PCB board whose copper layer is directly sintered to the ceramic substrate, the lamination temperatures are 1065℃-1085℃ (DBC direct bonded copper) or 700℃-900℃ (AMB active metal brazing).
Why use ceramic PCBs? Ceramic PCB boards feature stable and low Dk and Df, high-temperature resistance, high voltage resistance, excellent thermal conductivity, and impedance control with a small tolerance of 0.05%.
- Stable and low dielectric constant (Dk) of 9.3 and dissipation Factor (Df) of -4.
- Ceramics can endure high temperatures up to 2100℃, and ceramic PCB boards can work at high temperatures at 350℃ or even 800℃.
- Ceramics feature the best insulation properties and can withstand breakdown voltages up to 20KV/mm.
- Superior thermal conductivity: aluminum nitride PCBs 170-230W/mK, aluminum oxide PCBs 15-35W/mK.
- Ceramic PCB boards offer precise signal integrity with a precise impedance control tolerance of ±0.05%.
Knowing the pros of ceramic PCB boards, how about their drawbacks? The cons of ceramic PCBs are fragility and size restrictions.
Ceramics are easy to break so if a ceramic PCB is too big, it can break during lamination in the PCB manufacturing process.
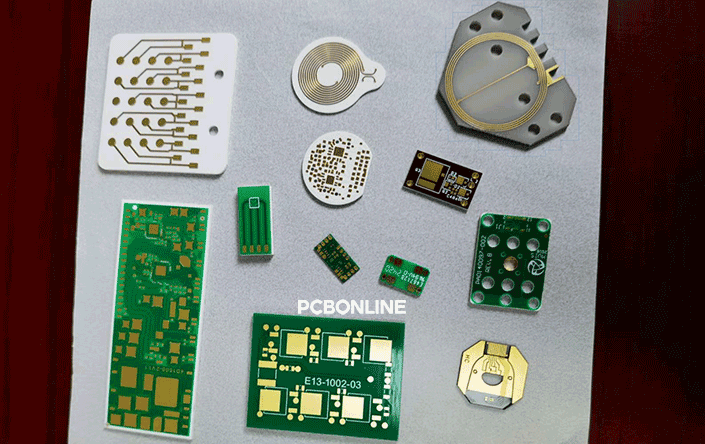
The maximum size of a ceramic PCB board is 138mm*190mm at the ceramic PCB manufacturer PCBONLINE.
Besides, though ceramic PCB boards can be made with 4 circuit layers, we suggest single-layer or double-sided two-layer ceramic PCB boards. That's because 4-layer ceramic PCBs are easy to break when we laminate one ceramic layer to the other.
How about PCB assembly for ceramic PCB boards?
Ceramic PCB assembly has no other differences with FR4 PCBs, but the reflow soldering temperature for ceramic PCB assembly reaches 400℃ and even 800℃.
Materials Used for Ceramic PCB Boards
With an understanding of ceramic PCB boards, now let's learn some details of the different ceramic PCB materials. Ceramic PCBs include aluminum nitride PCB (AlN PCB), aluminum oxide PCB (Al2O3 PCB), and BeO PCB.
Aluminum nitride (AlN PCB)

Thermal conductivity: 170-320 W/m·K
Advantages: High thermal conductivity, low expansion coefficient, and good mechanical strength.
Applications: Power modules, automotive electronics, and LED applications.
Aluminum oxide (Al2O3 PCB)

Thermal conductivity: 15-35W/m·K
Advantages: Cost-effective, good electrical insulation, and moderate thermal conductivity.
Applications: Communication electronics, voltage sensors, and inverters.
Beryllium oxide (BeO PCB)
Thermal conductivity: Up to 330 W/m·K
Advantages: High thermal performance and superior electrical insulation.
Applications: High-power electronic devices and defense applications.
PCBONLINE manufactures and assembles aluminum nitride PCBs and aluminum oxide PCBs. However, BeO powder is toxic for human beings, so it's extremely dangerous to manufacture BeO PCBs. That's why we don't provide BeO PCBs despite their best thermal conductivity.
Manufacturing Methods of Ceramic PCB Boards
The manufacturing methods for ceramic PCB boards include thick film, thin film, direct plating copper, LTCC, HTCC, AMB, and DBC.
Thick film ceramic PCB
Thick film ceramic PCB manufacturing involves depositing conductive pastes (such as silver, gold, and palladium silver) on the ceramic substrate by screen printing, and then sintering them at high temperatures to make them firmly adhere to the ceramic surface. The sintering temperature is 850℃-900℃, much higher than the lamination temperature of traditional organic substrate PCBs.
Thin film ceramic PCB
Thick film ceramic PCB manufacturing uses sputtering or evaporation to deposit thin metal layers.
They provide high precision and superior electrical performance and are ideal for RF and microwave applications.
Direct plating copper (DPC) PCB
DPC ceramic PCB manufacturing involves depositing copper layers directly onto the ceramic substrate.
They ensure excellent thermal conductivity and strong adhesion and are suitable for high-power LED applications.
Low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) PCB
LTCC ceramic PCB manufacturing uses multilayer lamination at temperatures below 900°C.
They allow complex circuit integration with embedded components and are applied in communication electronics and automotive sensors.
High-temperature co-fired ceramic (HTCC) PCB
HTCC ceramic PCB manufacturing processes ceramic at temperatures above 1600°C.
They offer high mechanical strength and durability and are used in aerospace and military electronics.
Active metal brazing (AMB) PCB
AMB ceramic PCB manufacturing involves bonding metal layers using active brazing materials.
They ensure strong thermal and mechanical bonding and are suitable for IGBT and power modules.
Direct bonded copper (DBC) PCB
DBC ceramic PCB manufacturing uses high-temperature oxidation to bond copper to ceramic.
They provide excellent heat dissipation and electrical performance and are common in power inverters and high-power semiconductor devices.
Applications of Ceramic PCB Boards
Ceramic PCB boards are used for power modules like IGBT, automotive electronics like voltage sensors and inverters, refrigeration sheets, solar energy storage, communication electronics, etc.
Power modules
Ceramic PCB boards are used in IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) modules for efficient power conversion.
They ensures stable operation under high current and voltage conditions.
Automotive electronics
Ceramic PCB boards are used in voltage sensors, inverters, and battery management systems.
Refrigeration and cooling systems
Ceramic PCB boards are integrated into thermoelectric cooling modules.
They provide effective heat dissipation for industrial refrigeration.
Solar energy storage
Ceramic PCB boards are used in solar inverters and power control systems.
They ensure energy efficiency and long-term stability.
Communication electronics
Ceramic PCB boards are used in RF, microwave, and high-frequency applications.
They provide minimal signal loss and high-speed data transmission.
Laser cutting
Ceramic PCBs are used in the laser cutting head of laser cut equipment. They are hard and can withstand cutting hard objects.
PCBONLINE: High-Quality Ceramic PCB Board Manufacturer
PCBONLINE is a one-stop ceramic PCB board manufacturer, providing turnkey AlN PCB and alumina PCB made by any of the above manufacturing methods. Besides, ceramic IGBT modules, ceramic COB LED modules, ceramic LED plates, etc, can also be provided by PCBONLINE.

PCBONLINE manufactures, assembles, and tests ceramic PCBs as a source factory manufacturer under one roof, from prototypes to bulky production.
PCBONLINE can manufacture ceramic PCBs to be HDI, high-frequency, multilayer, and double-sided.
Provides one-on-one free and professional DFM (design for manufacturing) for ceramic PCB boards before and during prototyping/sampling to ensure the success of your project and seamless mass production.
PCBONLINE has powerful ceramic PCB manufacturing capabilities. The copper layer thickness of ceramic PCBs is arbitrarily custom from 1μm to 1mm.
High-quality ceramic PCB boards with no oxide layer on the PCB surface have better welding performance and high-temperature resistance.
For ceramic PCB manufacturing and assembly orders at $5,000 and above, we offer free complete ceramic PCBA samples and functional tests. If you feel interested in ceramic PCB boards from PCBONLINE, feel free to send your inquiry by email at info@pcbonline.com.
Conclusion
This blog introduces ceramic PCB boards comprehensively. Aluminum nitride PCBs and alumina PCBs are mostly used ceramic PCB boards, while BeO PCBs are used much less. To manufacture ceramic PCB boards, the methods include thick film, thin film, DPC, LTCC, HTCC, DBC, and AMB. To ensure the success of your PCB/PCBA projects, work with the turnkey ceramic PCB manufacturer PCBONLINE.
PCB fabrication at PCBONLINE.pdf




