If you've ever had a PCB warp during reflow, fail EMI testing, or mysteriously drop signal strength in a high-speed circuit, there's a good chance PCB material selection played a role.
Choosing the right PCB material is one of those design decisions that's easy to overlook, but it's often the root of problems that show up late in the process, sometimes even after production. For engineers and designers, understanding your PCB material options isn't just helpful—it's essential.
Let's break down how to choose the right PCB materials in the real world.
Why Choosing the Right PCB Material Matters
Think of the PCB material as the foundation of your house. It supports everything—the layers, the copper traces, the components—and it determines how well your PCB board performs under stress, heat, frequency, or environmental exposure.
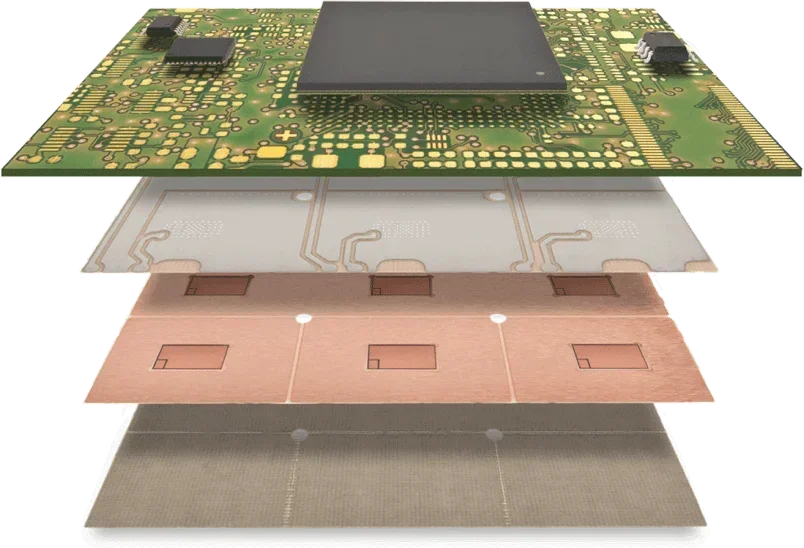
Whether you're designing a simple LED driver or a complex RF board, your PCB material affects these aspects:
- Signal integrity
- Thermal reliability
- Mechanical durability
- Manufacturability
- Cost and turnaround time
In short, if you care about performance, you need to care about the PCB material.
Start With the Right Questions about PCB Materials
Before you look at datasheets or talk to a PCB supplier, ask yourself:
- Will this PCB board carry high-speed or high-frequency signals?
- Is it going into a hot or harsh environment?
- Are there size constraints that require flex or rigid-flex PCB?
- Do I need tight impedance control?
- What's the budget? And how sensitive is it to cost changes?
Answering these helps narrow down your PCB material options fast.
Key PCB Material Properties to Understand
You don't need to be a chemist, but you should understand these terms when comparing PCB materials:
1. Tg (Glass Transition Temperature)
This is when the board's resin starts to soften. A board with a low Tg might warp during soldering or overheat in operation.
2. Td (Decomposition Temperature)
This is where the resin starts breaking down. For lead-free soldering (which goes up to 260°C), materials with Td above 300°C are safer bets.
3. CTE (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion)
Lower CTE = more stability under heat. High CTE can crack vias or break solder joints, especially in multilayer boards.
4. Dielectric Constant (DK)
Affects signal speed and impedance. Stable Dk is critical for RF and high-speed digital designs.
5. Dissipation Factor (Df)
Lower Df means less signal loss. If you're running above 1GHz, this matters a lot.
Common PCB Materials and When to Use Them
FR4
FR4 is the workhorse of the industry. It's cheap, widely available, and suitable for basic to mid-level designs. Standard FR4 is used widely for consumer electronics and general-purpose boards.
High-Tg FR4
Same as FR4, but high-Tg FR4 provides improved heat resistance. It's a smart upgrade for lead-free PCB assembly or thermally demanding applications, such as power supplies or automotive controllers.
The Tg of high-Tg PCB is 170℃ and above, while normal FR4 PCBs have a Tg of 130℃ to 150℃.
Rogers (RO4350B, RO4003C, etc.)
Used for RF and high-speed/high-frequency PCB boards where signal integrity is critical. Rogers materials offer low Dk (around 3.48) and stable thermal performance, making them ideal for high-frequency circuits. Many high-frequency materials produced by Rogers are PTFE-based composite materials, such as the common Rogers RO4000, RO3000, RT/duroid series, etc.
PTFE (Teflon-based)
These materials are soft, flexible, and offer a small, stable dielectric constant (Dk) and dissipation factor (Df). Dk ranges from 2.1 to 3.5 at 10 GHz, and Df is typically 0.0002 to 0.0005. Ideal for microwave and RF designs. Note: PTFE can be difficult to fabricate, so always check with your PCB manufacturer if they have the material in stock (sourcing may take up to three months) and confirm its storage time (within 45 days is recommended).
Polyimide
Polyimide (PI) is used in flexible and rigid-flex boards. Polyimide is known for its excellent flexibility and lightweight. It performs well in compact spaces that require flexibility and is preferred for aerospace, computer, communication, and wearable applications.
Ceramic
Ceramic offers the best thermal conductivity and can handle high voltages and high power levels. Ceramic PCBs are suitable for harsh environments, power electronics, and automotive modules.
Aluminum
Aluminum PCBs are mainly used for LED lighting due to their better thermal conductivity than FR4 and low cost. Aluminum dissipates heat efficiently, but there's a dielectric layer between the aluminum base and the circuit layers, so the CTE of the aluminum PCB is determined by the dielectric layer.
Copper
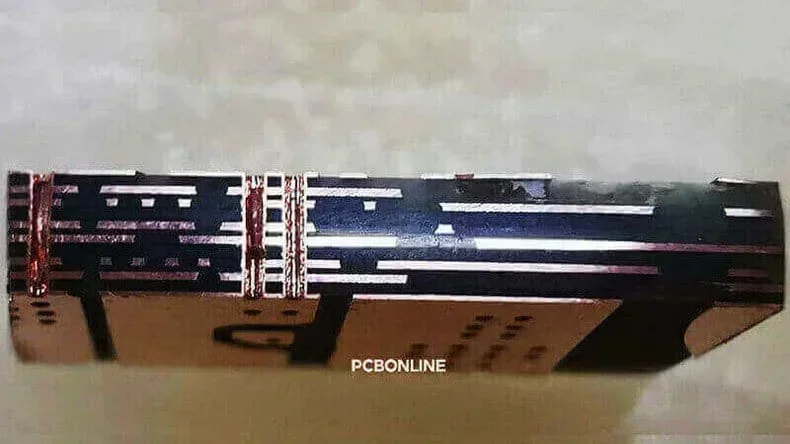

Copper provides superior conductivity and mechanical strength, allowing for robust and durable PCB designs. Copper-based PCBs dissipate thermal better than aluminum PCBs and are used in high-current circuits, power supplies, and motor controllers.
Other PCB materials
The less common PCB materials include flexible aluminum, polyester (PET), and glass. Flexible aluminum PCBs are used for LED lighting that needs flexibility, PET flex PCBs are clear flexible PCBs used for applications where transparency is required, and glass PCBs are alternatives to ceramic PCBs when the size constraint comes to leads to the breakage the break of ceramic PCBs during manufacturing.
Application-Based Recommendations
|
Application
|
Recommended Material
|
|
Basic consumer devices
|
FR4
|
|
Automotive electronics
|
High-Tg FR4 or Polyimide
|
|
RF/5G/High-frequency
|
Rogers, PTFE
|
|
Aerospace/satellite
|
Polyimide, PTFE, Ceramic
|
|
Industrial controls
|
High-Tg FR4 or Ceramic
|
|
Wearable/flexible tech
|
Polyimide (Flex or Rigid)
|
|
LED lighting
|
Aluminum, copper, or ceramic
|
|
Power electronics
|
Copper, high-Tg FR4 with heavy-copper circuits (with copper thickness above 3 oz/ft²), ceramic
|
What to Watch Out for when Selecting PCB Materials
Here are a few common mistakes designers make when it comes to choosing the PCB material.
- Ignoring thermal limits
- Assuming all FR4 is the same
- Skipping the fab consultation
Besides, here's a note on cost vs performance:
Everyone wants high-end PCB materials, but the truth is, you only need to upgrade when your design demands it.
One-stop Advanced PCB Manufacturer Helping Choose the Right PCB Material
If you're looking for a professional PCB manufacturer that can help choose the right PCB material and take part in R&D for your project, you can work with the advanced PCB manufacturer PCBONLINE for one-stop PCBA manufacturing and box-build assembly from prototypes to bulk production.

Founded in 1999, PCBONLINE has two large advanced PCB manufacturing bases, one turnkey PCB assembly factory for PCB assembly and box-build assembly, stable material supply chains and strategic cooperation with electronic component manufacturers, and long-term cooperation with the top 3 mold and enclosure manufacturers in China for jigs/fixtures, molds, and enclosures.
Besides, PCBONLINE has an R&D team and professional CAM engineers for project development and DFM (design for manufacturing).
PCBONLINE can manufacture PCBs made of any type of PCB materials, including FR4, high-Tg FR4, PI, PET, ceramic, Rogers, PTFE, aluminum, copper, glass, and hybrid substrates.
PCBONLINE has PTFE and Rogers materials in stock, which are stored within 45 days, saving the high-frequency PCB delivery time greatly.
Provides one-on-one free and professional DFM (design for manufacturing) for PCB, PCBA, and box-build projects, including choosing the right PCB material for your project in the early stage.
PCBONLINE manufactures, assembles, and tests from PCBs to box builds as a source factory manufacturer under one roof, from prototypes to bulky production.
High-quality PCBA manufacturing certified with ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, IATF 16949:2016, RoHS, REACH, UL, and IPC-A-610 Class 2/3.
When your project goes to the bulky production stage, PCBONLINE reduces the fees of prototyping, including its value-added services.
By working with the one-stop PCBA manufacturer PCBONLINE, you don't need to find other providers for value-added services, components, tests, jigs, and enclosures, as all these can be provided by PCBONLINE. No matter what materials your PCB uses and what application the PCB will be used for, such as automotive, industrial control, medical, military, aerospace, communication, agriculture, etc, you can work with PCBONLINE. To get a quote for your project to the turkey PCBA manufacturer PCBONLINE, contact info@pcbonline.com.
Conclusion
PCB material selection isn't flashy, but it's one of the smartest decisions you can make early in your design process. It impacts everything downstream—from signal quality to yield to how long your PCB board lasts in the field.
With the right material, your board performs better, lasts longer, and makes your life a whole lot easier. To ensure the success of your PCB and PCBA project with professional DFM and high quality, work with the one-stop advanced PCB manufacturer PCBONLINE.
PCB fabrication at PCBONLINE.pdf




