The European Union's RoHS standards require all electronic products to be lead-free (Pb < 0.1%), and similar lead-free standards are also regulated in the US, Canada, China, etc. Lead-free is a systematic requirement, including lead-free components, lead-free PCBs, lead-free reflow soldering, etc.
Lead-free reflow soldering is a key process during lead-free PCB assembly. This article gives a comprehensive introduction to lead-free reflow soldering, including the lead-free reflow profile, reliable lead-free assembly solution, and the advantages of lead-free reflow.
Part 1. What is Lead-Free Reflow
![]()
Lead-free reflow soldering is the process of adjusting reflow oven temperatures to melt and cure lead-free solder paste on the PCB pads during PCB assembly. When the PCBAs cool down, the SMD components are soldered on the PCB pads.
Lead-free reflow is fully automatic and happens in the lead-free reflow oven, which has ten temperature chambers (tin-lead reflow oven has eight). The reflow oven raises the temperatures by heating nitrogen gas. In the lead-free reflow oven, the PCBAs are transferred by the conveyor belt and undergo four stages:
1. Preheat stage
When the PCBAs go into the lead-free reflow oven, they are preheated slowly at a uniform rate to remove the moisture and solvent in the solder paste. The other reason for this is preparation for reflow to avoid thermal shock and harm to the SMD components, insufficient soldering on PCB pads, solder balls in non-soldering areas, and spattering.
Lead-free reflow preheat temperatures reach about 150°C to 190°C, and the preheat slope rate is about 0.75℃/sec to 2℃/sec. The lead-free reflow preheat stage lasts about 60 seconds to 120 seconds.
2. Soak stage
The reflow soak stage is the step where the solder paste removes moisture, and the flux activates so it can solder. The oxide on the surfaces of components and PCB pads is also removed. The temperatures during the soak stage increase slower than during the preheat stage.
Lead-free reflow soaking temperatures reach about 217°C, and the temperature increase slope rate is about 0.5℃/sec to 1℃/sec. The lead-free soak stage lasts about 60 seconds to 120 seconds.
3. Reflow soldering stage
The reflow stage is the step when the solder paste completely reflows. Lead-free reflow temperatures reach about 240°C to 248°C, and before the temperatures reach the peak, the alloy powder melts and soaks the PCB pads and components. The reflow oven remains at the peak temperatures for some time so the alloy liquid reflows and the whole PCBA has an even temperature in case of tombstoning.
The lead-free reflow stage lasts about 40 seconds to 70 seconds, and the peak temperature lasts for about 10 seconds to 30 seconds.
3. Cooling stage
The reflow cooling stage is the step where the solder consolidates as the reflow oven zones' temperatures get down from the peak to 75°C, and the components and PCB pads are well soldered. The cooling slope rate should be about twice the preheat slope rate to avoid PCB parts bending and burrs on the solder joints.
Part 2. Lead-Free Reflow Profile
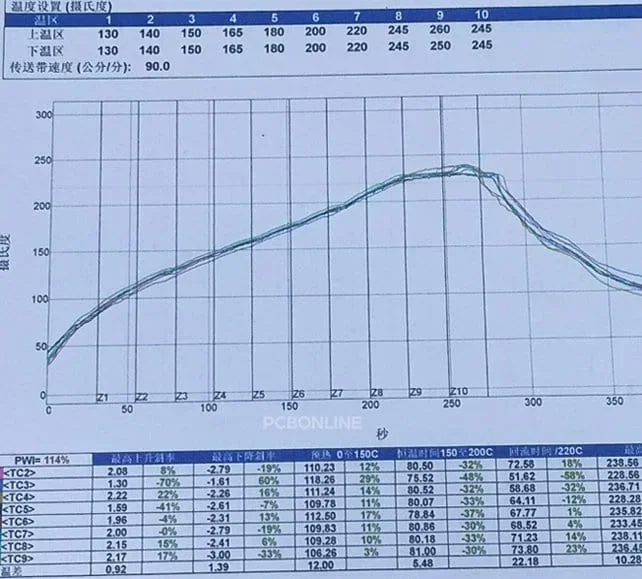
A lead-free reflow soldering profile is made according to the temperature data collected from the reflow oven temperature testing board, which is connected to the DATAPAQ and goes through the reflow oven.
A lead-free reflow profile reflects the above 4 stages in the reflow process. The lead-free reflow profile specifications depend on the solder paste melting point and the highest temperature that the PCB laminate can bear.
The commonly seen lead-free solder paste uses the alloy powder Sn96.5Ag3Gu0.5, which has a melting point of 217°C. A lead-free reflow profile using this lead-free solder paste is below:
![]()
You may need to read the below specifications table to better understand the above lead-free reflow profile.
|
Lead-free reflow profile features
|
Specifications
|
|
Preheat rate
|
0.75℃/s to 2℃/s
|
|
Preheat time
|
60s to 120s
|
|
Preheat temperatures
|
150℃ to 190℃
|
|
Temperature increase rate in the soaking stage
|
0.5℃/s to 1℃/s
|
|
Soaking time
|
60s to 120s
|
|
Soaking temperatures
|
217℃
|
|
Reflow temperatures
|
Higher than 217℃
|
|
Reflow time
|
40s to 70s
|
|
Reflow peak temperatures
|
240℃ to 248℃
|
|
Reflow peak time
|
10s to 30s
|
|
Cooling rate
|
1.5℃/s to 4℃/s
|
|
Cooling temperatures
|
Cooling from the peak temperature to 75℃
|
|
Conveyor speed
|
70cm/min
|
The lead-free reflow profile is tailored according to the PCB substrate, copper thickness, components' thermal withstand abilities, and the melting point of solder paste.
As an OEM manufacturer, research institute, or business maker, you don't need to worry about the specifications of the lead-free reflow profile, as the PCBA manufacturer such as PCBONLINE can design it with expertise and experience.
Part 3. Lead-Free Reflow vs. Tin-Lead Reflow
Lead-free reflow is different from the traditional tin-lead reflow soldering in:
- 1. Lead-free reflow requires using lead-free solder paste, such as tin-copper alloy solder paste, or tin-silver alloy solder paste.
- 2. The lead-free reflow temperatures are about 30°C higher than the traditional tin-lead reflow temperatures.
- 3. Lead-free reflow ovens can handle both lead-free assembly and lead-tin assembly. Lead-tin reflow ovens can't assemble lead-free PCBs.
- 4. Tin-lead reflow allows the reflow temperature fluctuation range of 30°C, but the lead-free reflow allows the reflow temperature fluctuation range of only 5°C.
- 5. The lead-free reflow heating rate is higher than that of the lead-tin reflow. Lead-free reflow has more difficulty than tin-lead reflow.
Part 4. Advantages of Lead-Free Reflow Soldering
Compared with traditional tin-lead PCB reflow soldering, lead-free reflow soldering has these pros:
- 1. The nitrogen gas flows more evenly in the lead-free reflow process than in the tin-lead reflow. This reduces the temperature tolerances on the PCB boards and achieves a better soldering effect.
- 2. Lead-free reflow oven can be used for lead-free reflow, tin-lead reflow, chip aging, and red glue curing.
- 3. The temperature control of the lead-free reflow is more precise than the tin-lead reflow and is about ±2℃.
- 4. The lead-free reflow is non-toxic, has less pollution than tin-lead reflow, and realizes the recycling of nitrogen.
Part 5. Lead-Free Reflow PCB Soldering One-Stop Solution - PCBONLINE
PCBONLINE is a one-stop advanced PCB manufacturer founded in 1999, with two large PCB manufacturing bases and one PCB assembly factory. PCBONLINE provides turnkey lead-free PCB assembly from prototypes to bulky production, including lead-free PCB manufacturing, electronic component sourcing, lead-free PCB assembly, and value-added services such as conformal coating, IC programming, and end-product assembly.

PCB manufacturing and assembly from PCBONLINE are compliant with ISO, IATF, REACH, RoHS, UL, and IPC standards.
IPC-A-610 Class 2/3 high-quality lead-free PCB assembly including SMT and THT for automotive, medical, industrial, communication, defense, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
One-on-one engineering support for your lead-free projects, with free DFM, DFT, and DFX.
The whole EMS process is lead-free, including electronic components, PCB manufacturing, PCB assembly, and shipping.
Best-price lead-free electronic components sourced from direct component factories, no refurbished parts.
Free complete PCBA samples and functional testing for bulky PCB assembly orders.
Please feel free to send your BOM and Gerber file to PCBONLINE by email at info@pcbonline.com to get a quote for lead-free PCB assembly.
Conclusion
This article gives a detailed illustration of SMD polarity and identification methods for the polarity of capacitors, inductors, LEDs, diodes, and ICs. If you still have problems with SMD polarity, welcome to leave your question via our online chatting window on the right of the PCBONLINE webpage. If you need SMD components or PCB assembly, do not miss PCBONLINE, the 23-year-old source factory.
PCB assembly at PCBONLINE.pdf




