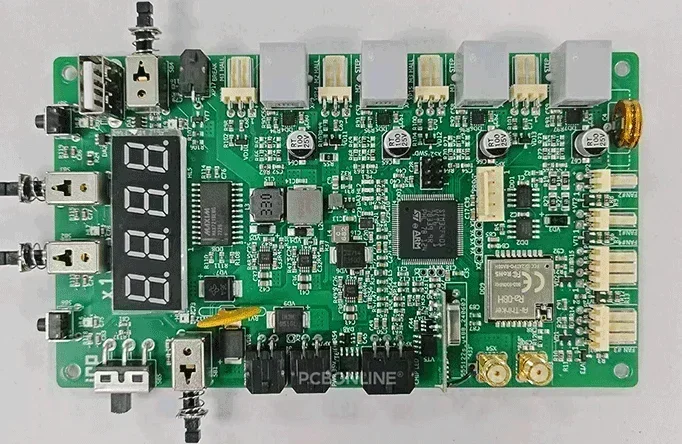
Block-like electronic components are mounted on the surface of an assembled printed circuit board (PCB).
These electronic components are Surface Mount Devices (SMDs). In this blog, we will learn about SMD electronic components, SMD sizes, some common SMD components, the SMT process, and the value they provide.
In this article:
Part 1. What are SMD Electronic Components Part 2. SMD Electronic Component Sizes Part 3. Common SMD Electronic Components Part 4. Assembly of SMD Components Part 5. One-Stop PCBA Manufacturer PCBONLINEWhat are SMD Electronic Components
Surface mount devices or SMDs are the electronic components that are directly placed and soldered on the surface of the PCBs.
The SMDs have smaller sizes than through-hole devices, whereas the through-hole devices take more space on the PCB, resulting in higher costs.
The following table compares the SMD electronic components and through-hole devices.
SMD components vs. through-hole components
|
Aspect
|
SMD electronic components
|
Through-hole components
|
|
Mounting style
|
Directly onto the surface of the PCB
|
Leads are inserted into the holes and soldered
|
|
SMD component size
|
Smaller and more compact
|
Larger and bulkier
|
|
PCB space usage
|
Saves space and requires no drilling
|
Requires more space due to leads and hole–drilling
|
|
Assembly speed
|
Faster, and automated using machines
|
Slower because of manual or semi-manual assembly
|
|
Mechanical strength
|
Lower; prone to stress if handled roughly
|
Higher; better suited for harsh or rugged environments
|
|
Cost of production
|
Lower for bulky production due to automation
|
Higher for bulky production due to manual labor and jig use
|
|
Application
|
Ideal for high-density, compact electronics
|
For products requiring higher mechanical durability and power
|
|
Heat dissipation
|
Lower due to small sizes
|
Better heat dissipation, specially for power components
|
|
Manufacturing technology
|
Suitable for automated mass production
|
More labor-intensive, suited for prototyping or low-volume production
|
From the above table, we can see that the SMD electronic components offer many advantages over through-hole components, especially their compact sizes.
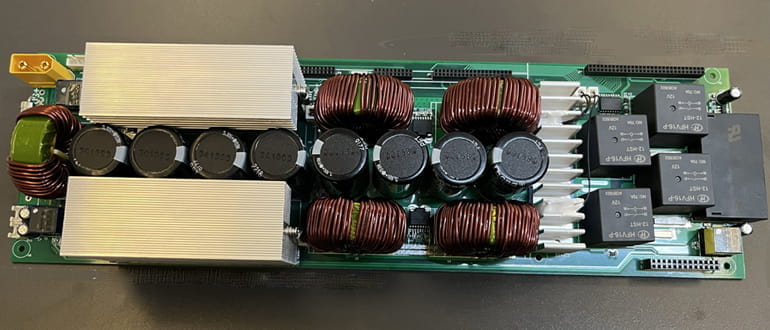
Figure: Through-hole components assembled on a PCB
Let's look at the different sizes of the SMDs.
SMD Electronic Component Sizes
The SMD components come in various sizes, and they use the numeric coding system (like 01005,0402, etc.) to indicate their physical dimension. The format for these codes is:
LLWW
LL = the length of the component in hundredths of an inch
WW = the width of the component in hundredths of an inch
For example, 01005 can break down into:
Length = 01 x 0.01 = 0.01 inches
Width = 005 means 0.5 x 0.01 = 0.005 inches
Similarly, 0603 can break down into:
Length = 06 x 0.01 = 0.06 inches
Width = 03 x 0.01 = 0.03 inches
The above-mentioned sizes were in the Imperial coding system. Now let's look at the common sizes (Imperial code) of the SMD and their applications.
|
Aspect
|
SMD electronic components
|
Through-hole components
|
Through-hole components
|
|
01005
|
0.01
|
0.005
|
Extremely small, used in ultra-high-density designs.
|
|
0201
|
0.02
|
0.01
|
Very small, and used in compact and precise electronics.
|
|
0402
|
0.04
|
0.02
|
Slightly small, but still suited for tight applications.
|
|
0603
|
0.06
|
0.03
|
A common size for general-purpose SMD components.
|
|
0805
|
0.08
|
0.05
|
Larger, offering better power handling and easier assembly.
|
|
1206
|
0.12
|
0.06
|
Widely used in industrial and power electronics.
|
|
1210
|
0.12
|
0.10
|
Large, often used for capacitors and resistors in power circuits.
|
Besides the imperial coding system for representing the sizes of SMD electronic components, there is the metric coding system. It uses millimeters instead of inches for the SMD size units.
To convert inches to millimeters, you can use the conversion equivalent:
1 inch = 25.4 millimeters
For example,
01005 represents 0.01" × 25.4 = 0.254mm length and 0.005" × 25.4 = 0.127mm width.
0201 represents 0.02" × 25.4 = 0.508mm length and 0.01" × 25.4 = 0.254 mm width.
Relationship between SMD Sizes and PCB Footprints
Each SMD size corresponds to a specific PCB footprint, which is the designated area on the PCB, where the components will be soldered.
The footprint ensures that the SMD electronic component is securely attached and properly aligned
The PCB footprint for an SMD component includes the pads where soldering occurs, and it is designed to match the component's dimensions.
For instance, a 0603 SMD size will have a footprint with pads that accommodates a length (0.06" x 25.4 = 1.54mm rounded off to) 1.60 mm and a width of (0.03" in x 25.4=0.76mm rounded off to) 0.80mm.
SMD sizes are directly proportional to the PCB footprints. The smaller components such as 01005 or 0201 require smaller footprints, whereas larger components such as 1206 or 1210 require bigger PCB footprints.
To summarize the relationship, SMD sizes influence the PCB footprint, which in turn affects the overall PCB size and design. Smaller SMDs contribute to a more compact PCB, whereas larger SMDs provide easier handling and better heat dissipation.
Now let's view the common SMD components.
Common SMD Electronic Components
SMD components vary not only in size but also in type, each serving specific purposes in electronic circuits, ranging from simple signal processing to complex integration. Here is a brief overview of common SMD components and their typical use:
SMD LEDs
SMD LEDs are compact light-emitting diodes used for indicators and displays. They provide feedback in electronic devices.
SMD LEDs have different types based on the size and brightness of the LED. For example, SMD LED 352 is known for its power output of 6 to 8 lumens and a consumption of just 0.20W, offering a low light output suitable for specific applications.
They are small, rectangular, or oval-shaped packages with two or more terminals as shown in the following figure.

Figure: SMD LED and LED schematic symbol
SMD resistors
SMD resistors control the current flow in the circuits. They limit current and divide voltage. They are flat, rectangular packages with two terminals on the short sides as shown in the following image (R100 represents 100 ohms).

Figure: SMD resistors and resistor schematic symbol
SMD capacitors
SMD capacitors store and filter electrical charge. They are used for stabilizing voltages and filtering noise, ensuring smooth operation of electronic circuits.
SMD capacitors are flat, rectangular, or square packages with two terminals on short sides as shown in the following figure (270 represents 27 pF).
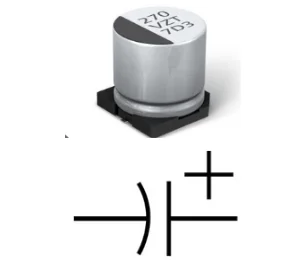
Figure: SMD capacitor and capacitor schematic symbol
SMD diodes
Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only and are used for protection and rectification.
SMD diodes are small and rectangular packages with two terminals as shown in the following figure.
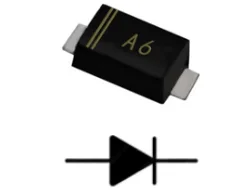
Figure: SMD Diode and Diode schematic symbol
SMD transistors
Transistors amplify or switch electronic signals. They regulate electronic signals and power various parts of a circuit.
SMD transistors typically have three terminals and are rectangular or square as shown in the following figure.
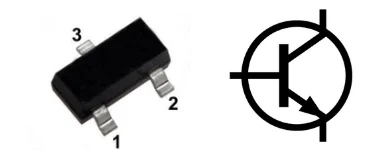
Figure: SMD Transistor and Transistor schematic symbol
SMD ICs
Integrated circuits combine multiple functions into a single package. They control and manage the circuit as the core components.
ICs often have a large number of pins or pads for connections as shown in the below figure.

Figure: SMD Integrated Circuit (IC)
Assembly of SMD Components
To assemble the SMD components on the PCB, a process called surface mount technology (SMT) is used.
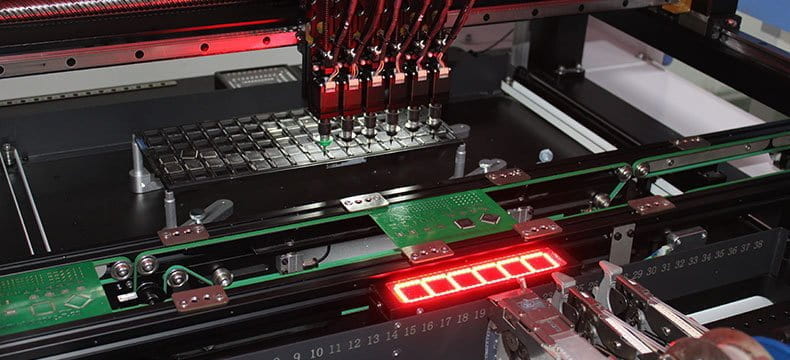
SMT assembly is fully automated and continuous. Here are the key steps involved in the SMT process.
- Solder paste printing: Solder paste is applied to the PCB's pads with an SMT stencil. The thickness, position, and size of the paste are inspected for quality control.
- Component placement: SMD electronic components are placed onto the PCB using high-speed mounters for small components and functional mounters for larger ones.
- X-ray inspection: An X-ray machine is used to detect the solder balls of the BGA.
- Reflow soldering: After placement, the PCB with SMD components is passed through a reflow oven. In this process, the solder paste is heated to melt and form solid solder joints with the copper pad.
- Automated optical inspection (AOI): 3D AOI is used to detect any surface defects of the PCBA. The AOI machine is in the SMT line.
The above process explains how the SMD electronic components are assembled on the PCB. After SMT assembly, the PCB is soldered with through-hole components on the other production line - the PTH line.
One-Stop PCBA Manufacturer PCBONLINE
Whether you want to buy SMD electronic components or electronic manufacturing and assembly, you can do it at PCBONLINE.

PCBONLINE is a one-stop PCBA manufacturer, providing advanced PCB fabrication, SMD and PTH component sourcing, PCB assembly, value-added services (IC burn-in, conformal coating...), and box-build assembly to be the final products.
A source factory PCBA manufacturer, having two large advanced PCB manufacturing bases, one PCB assembly factory, stable supply chains, and an R&D team.
PCBONLINE purchases bulky THT and SMD electronic components directly from the original component factories and first-class suppliers that have been audited by us, and all the components are traceable.
PCBONLINE can join co-procurement with other EMS manufacturers for electronic components at lower prices.
For SMD electronic component mounting, PCBONLINE offers SMT assembly, with X-ray inspection, 3D AOI, and lead-free or nitrogen reflow soldering to ensure high quality.
PCBA manufacturing from PCBONLINE is certified with ISO 9001:2015, ISO14001:2015, IATF 16949: 2016, RoHS, REACH, UL, and IPC-A-610 Class 2/3.
We offer free and comprehensive DFM (design for manufacturing) for all projects, including checking the BOM, SMDs, and PCB footprints to ensure the correct materials and component orientation and solving all issues during prototyping to ensure a smooth electronics manufacturing process.
To get a quote for the SMD electronic components and PCBA manufacturing for your project, don't hesitate to contact info@pcbonline.com.
Conclusion
Understanding SMD electronic components is crucial for designing and manufacturing modern electronic devices. Using the SMDs, surface mount technology (SMT) achieves compact design capabilities. For high-quality SMD PCB fabrication and assembly, work with the one-stop advanced PCBA manufacturer PCBONLINE.
PCB assembly at PCBONLINE.pdf




